|
|
《ACNet: Strengthening the Kernel Skeletons for Powerful CNN via Asymmetric Convolution Blocks》
paper:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Ding_ACNet_Strengthening_the_Kernel_Skeletons_for_Powerful_CNN_via_Asymmetric_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf
下图是整个ACNet的核心. ACNet将常规的3x3卷积替换成了3x3卷积、1x3卷积和3x1卷积的并行结构,重在训练阶段提升模型的特征提取能力,推理时利用结构重参数化技术重新将三分支的并行状态融合成单分支的3x3卷积. 这个方式会增加模型训练时间,但能够在推理时无痛涨点. 【个人观点:我更愿意将ACNet理解为一种训练策略,而不是一个模型】
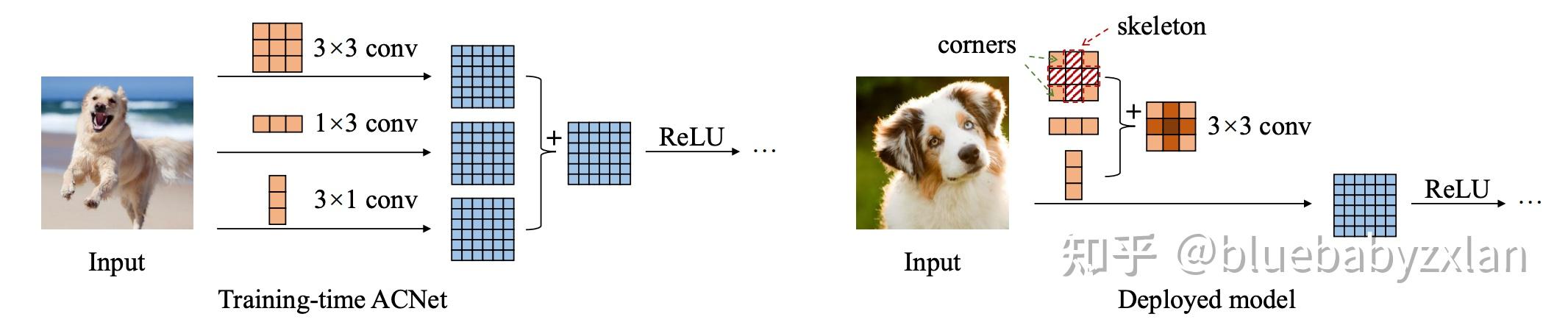
ACNet核心点
highlight
- 提出ACB(Asymmetric Convolution Block),将3x3卷积修改成3x3卷积、1x3卷积和3x1卷积的并行结构. 1x3卷积和3x1卷积可以分别加强模型对垂直翻转、水平翻转的不变性. 即强化卷积skeleton的特征提取能力.
- 训练完成后,利用结构重参数化技术,将ACB重新替换成3x3卷积,不增加推理时的参数量、计算量和推理速度.
- ACB可以替换掉任意的、现有的网络结构中的卷积核,而实现推理时的无痛涨点,可迁移性很强.
ACB简介
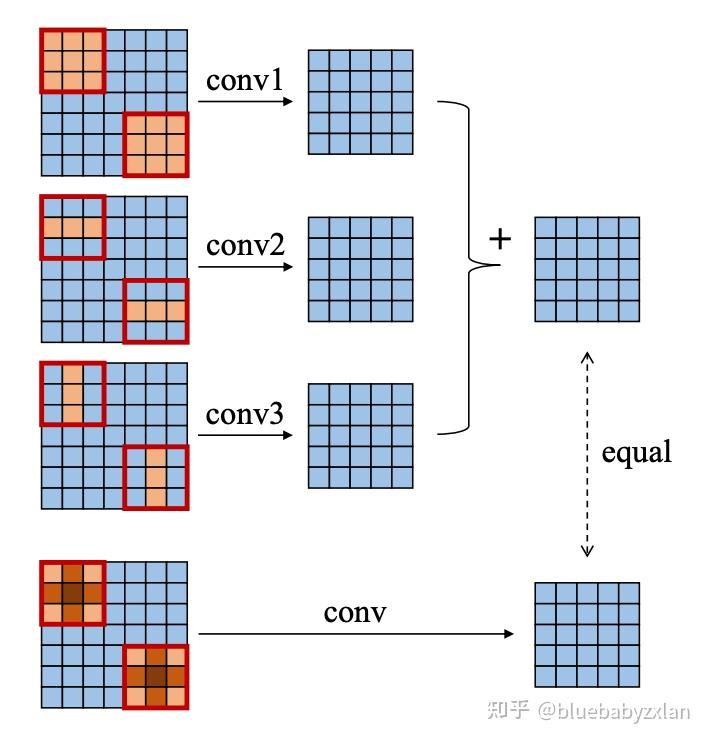
ACB的内容很简单,也就是上文所提及的将常规的3x3卷积修改成3x3卷积、1x3卷积和3x1卷积的并行结构. 但这里有一个注意点是1x3卷积和3x1卷积的feature map卷积内容. 对于3x3卷积来说,通常为了保证输入和输出的形状保持一致,会对输入的feature map进行padding. 而在卷积滑窗的过程中,1x3卷积或3x1卷积的位置应始终对应的是3x3卷积skeleton的位置,这样才能保证结构重参数化时的参数对应关系. 这里主要体现在卷积开始行列的位置和结束行列的位置. 例如,1x3卷积在padding的情况下,应该从第二行(第一行为zero-padding)开始,到倒数第二行(倒数第一行为zero-padding)结束. 类似的,3x1卷积在padding的情况下,也应该从第二列(第一列为zero-padding)开始,到倒数第二列(倒数第一列为zero-padding)结束.
上述1x3卷积和3x1卷积的位置对应关系,看似有点麻烦,但在实现时可以采用重新计算padding的方式来完成. 如3x3卷积的padding=(1, 1),那么就可以计算得到1x3卷积padding=(0, 1),3x1卷积padding=(1, 0). 依照此思路即可实现上述的位置对应关系.
ACB测试时融合的方式如下图所示. 我们不仅可以融合ACB为一个3x3卷积,还可以将后续的BN层也一起融合进来. 众所周知,BN在测试时也可视作一个线性函数 y = \alpha x + \beta ,只需将卷积得到的output代到BN公式中即可实现重参数. 融合完并行结构中各分支的卷积和BN,即可把三个分支的结果重新做一个相加整理. 这里由于 \mu, \gamma, \sigma, \beta 都是已求得的已知数,故可以直接做相加后视作偏置b.
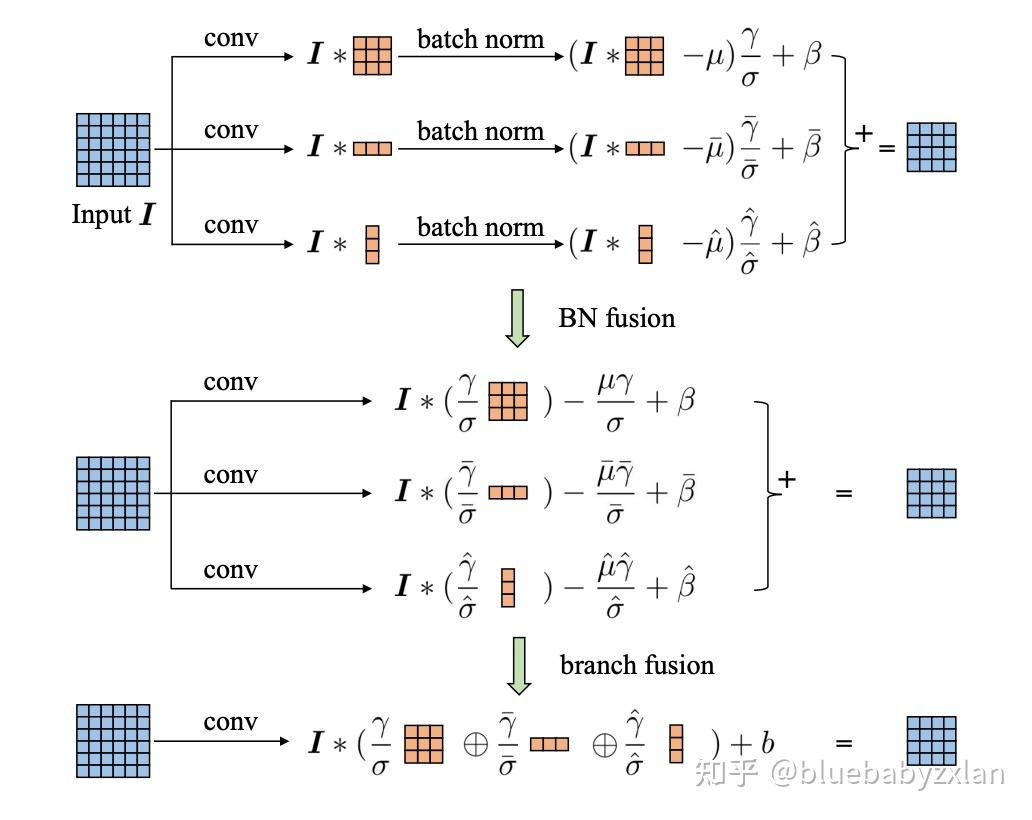
ACB测试时融合
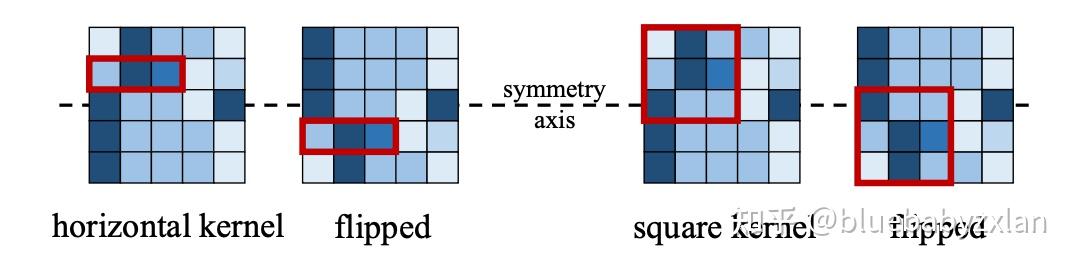
为什么说ACB具有提高模型的翻转不变性?如下图所示,在对原图进行垂直翻转后,1x3卷积的input保持不变. 而正常的3x3卷积的input则发生了改变.
这里我个人认为更好的理解是卷积核3x3各位置上的weights是不同的,因此当input的位置发生了调换时,input * weight就会得出不同的结果,而这种结果还可能会因为网络层数的叠加发生更大的改变.
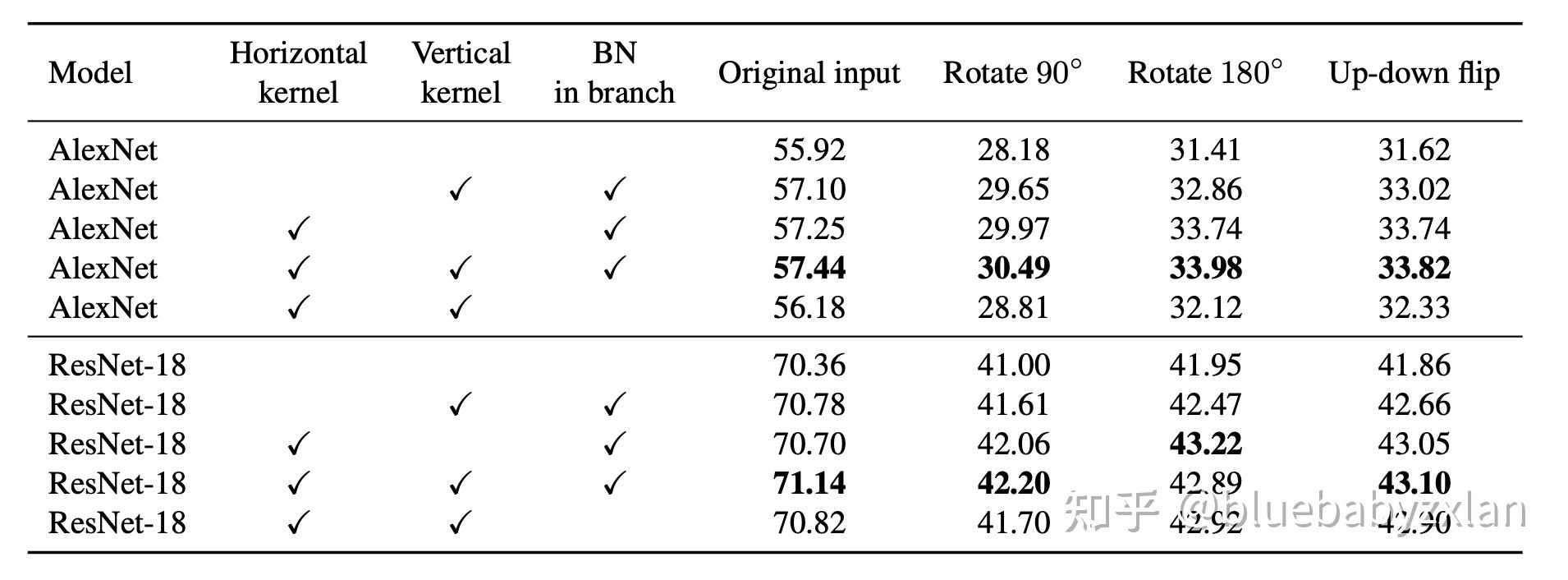
文章实验结果也证实了关于ACB提高翻转不变性这一点,结果如下.
代码实现
该部分来自ACNet的官方代码实现. https://github.com/DingXiaoH/ACNet/blob/master/acnet/acb.py import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.init as init
import torch
class ACBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', deploy=False,
use_affine=True, reduce_gamma=False, gamma_init=None ):
super(ACBlock, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy
if deploy:
self.fused_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(kernel_size,kernel_size), stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True, padding_mode=padding_mode)
else:
self.square_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=(kernel_size, kernel_size), stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False,
padding_mode=padding_mode)
self.square_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, affine=use_affine)
if padding - kernel_size // 2 >= 0:
# Common use case. E.g., k=3, p=1 or k=5, p=2
self.crop = 0
# Compared to the KxK layer, the padding of the 1xK layer and Kx1 layer should be adjust to align the sliding windows (Fig 2 in the paper)
hor_padding = [padding - kernel_size // 2, padding]
ver_padding = [padding, padding - kernel_size // 2]
else:
# A negative &#34;padding&#34; (padding - kernel_size//2 < 0, which is not a common use case) is cropping.
# Since nn.Conv2d does not support negative padding, we implement it manually
self.crop = kernel_size // 2 - padding
hor_padding = [0, padding]
ver_padding = [padding, 0]
self.ver_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(kernel_size, 1),
stride=stride,
padding=ver_padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False,
padding_mode=padding_mode)
self.hor_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(1, kernel_size),
stride=stride,
padding=hor_padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False,
padding_mode=padding_mode)
self.ver_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, affine=use_affine)
self.hor_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, affine=use_affine)
if reduce_gamma:
self.init_gamma(1.0 / 3)
if gamma_init is not None:
assert not reduce_gamma
self.init_gamma(gamma_init)
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, conv, bn):
std = (bn.running_var + bn.eps).sqrt()
t = (bn.weight / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return conv.weight * t, bn.bias - bn.running_mean * bn.weight / std
def _add_to_square_kernel(self, square_kernel, asym_kernel):
asym_h = asym_kernel.size(2)
asym_w = asym_kernel.size(3)
square_h = square_kernel.size(2)
square_w = square_kernel.size(3)
square_kernel[:, :, square_h // 2 - asym_h // 2: square_h // 2 - asym_h // 2 + asym_h,
square_w // 2 - asym_w // 2: square_w // 2 - asym_w // 2 + asym_w] += asym_kernel
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
hor_k, hor_b = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.hor_conv, self.hor_bn)
ver_k, ver_b = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.ver_conv, self.ver_bn)
square_k, square_b = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.square_conv, self.square_bn)
self._add_to_square_kernel(square_k, hor_k)
self._add_to_square_kernel(square_k, ver_k)
return square_k, hor_b + ver_b + square_b
def switch_to_deploy(self):
deploy_k, deploy_b = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.deploy = True
self.fused_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.square_conv.in_channels, out_channels=self.square_conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.square_conv.kernel_size, stride=self.square_conv.stride,
padding=self.square_conv.padding, dilation=self.square_conv.dilation, groups=self.square_conv.groups, bias=True,
padding_mode=self.square_conv.padding_mode)
self.__delattr__(&#39;square_conv&#39;)
self.__delattr__(&#39;square_bn&#39;)
self.__delattr__(&#39;hor_conv&#39;)
self.__delattr__(&#39;hor_bn&#39;)
self.__delattr__(&#39;ver_conv&#39;)
self.__delattr__(&#39;ver_bn&#39;)
self.fused_conv.weight.data = deploy_k
self.fused_conv.bias.data = deploy_b
def init_gamma(self, gamma_value):
init.constant_(self.square_bn.weight, gamma_value)
init.constant_(self.ver_bn.weight, gamma_value)
init.constant_(self.hor_bn.weight, gamma_value)
print(&#39;init gamma of square, ver and hor as &#39;, gamma_value)
def single_init(self):
init.constant_(self.square_bn.weight, 1.0)
init.constant_(self.ver_bn.weight, 0.0)
init.constant_(self.hor_bn.weight, 0.0)
print(&#39;init gamma of square as 1, ver and hor as 0&#39;)
def forward(self, input):
if self.deploy:
return self.fused_conv(input)
else:
square_outputs = self.square_conv(input)
square_outputs = self.square_bn(square_outputs)
if self.crop > 0:
ver_input = input[:, :, :, self.crop:-self.crop]
hor_input = input[:, :, self.crop:-self.crop, :]
else:
ver_input = input
hor_input = input
vertical_outputs = self.ver_conv(ver_input)
vertical_outputs = self.ver_bn(vertical_outputs)
horizontal_outputs = self.hor_conv(hor_input)
horizontal_outputs = self.hor_bn(horizontal_outputs)
result = square_outputs + vertical_outputs + horizontal_outputs
return result
if __name__ == &#39;__main__&#39;:
N = 1
C = 2
H = 62
W = 62
O = 8
groups = 4
x = torch.randn(N, C, H, W)
print(&#39;input shape is &#39;, x.size())
test_kernel_padding = [(3,1), (3,0), (5,1), (5,2), (5,3), (5,4), (5,6)]
for k, p in test_kernel_padding:
acb = ACBlock(C, O, kernel_size=k, padding=p, stride=1, deploy=False)
acb.eval()
for module in acb.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.uniform_(module.running_mean, 0, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform_(module.running_var, 0, 0.2)
nn.init.uniform_(module.weight, 0, 0.3)
nn.init.uniform_(module.bias, 0, 0.4)
out = acb(x)
acb.switch_to_deploy()
deployout = acb(x)
print(&#39;difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is&#39;)
print(((deployout - out) ** 2).sum())输出结果:
input shape is torch.Size([1, 2, 62, 62])
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(4.7047e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(3.1643e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(7.5074e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(7.6837e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(8.0299e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(7.0121e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
difference between the outputs of the training-time and converted ACB is
tensor(8.0450e-10, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>) |
|